Generate Ssl Key And Certificate
If you want to convert your website from HTTP to HTTPS, you need to get a SSL certificate from a valid organization like Verisign or Thawte. You can also generate self signed SSL certificate for testing purpose.
In this article, let us review how to generate private key file (server.key), certificate signing request file (server.csr) and webserver certificate file (server.crt) that can be used on Apache server with mod_ssl.
- Ssl Certificate Generate Windows
- Generate Ssl Key And Certificate Free
- Ssl Certificate Generate Private Key
- Generate Ssl Key And Certificate Registration
Key, CSR and CRT File Naming Convention
Apr 09, 2020 SSL – Secure Socket Layer; TLS – Transport Layer Security; Certificate Creation Workflow. Following are the steps involved in creating CA, SSL/TLS certificates. CA Key and Certificate Creation. Generate a CA private key file using a utility (OpenSSL, cfssl etc) Create the CA root certificate using the CA private key. Server Certificate. Step Two: Create a New Certificate. Now that Apache is ready to use encryption, we can move on to generating a new SSL certificate. The certificate will store some basic information about your site, and will be accompanied by a key file that allows the server to securely handle encrypted data.
I typically like to name the files with the domain name of the HTTPS URL that will be using this certificate. This makes it easier to identify and maintain.
- Instead of server.key, I use www.thegeekstuff.com.key
- Instead of server.csr, I use www.thegeekstuff.com.csr
- Instead of server.crt, I use www.thegeekstuff.com.crt
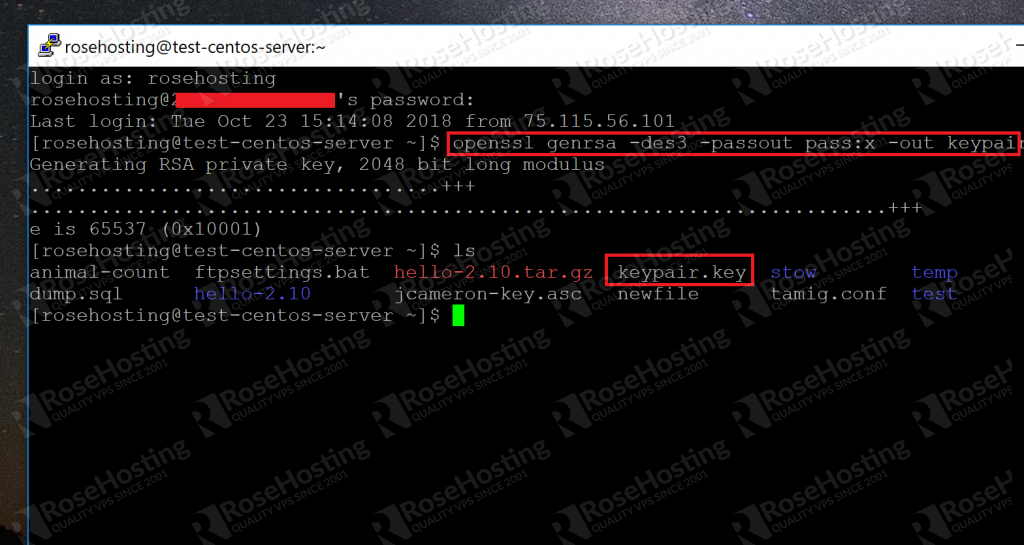
1. Generate Private Key on the Server Running Apache + mod_ssl
First, generate a private key on the Linux server that runs Apache webserver using openssl command as shown below.
The generated private key looks like the following.
2. Generate a Certificate Signing Request (CSR)
Using the key generate above, you should generate a certificate request file (csr) using openssl as shown below.
3. Generate a Self-Signed SSL Certificate
For testing purpose, you can generate a self-signed SSL certificate that is valid for 1 year using openssl command as shown below.
You can use this method to generate Apache SSL Key, CSR and CRT file in most of the Linux, Unix systems including Ubuntu, Debian, CentOS, Fedora and Red Hat.
4. Get a Valid Trial SSL Certificate (Optional)
Instead of signing it youself, you can also generate a valid trial SSL certificate from thawte. i.e Before spending the money on purchasing a certificate, you can also get a valid fully functional 21 day trial SSL certificates from Thawte. Once this valid certificate works, you can either decide to purchase it from Thawte or any other SSL signing organization.
This step is optional and not really required. For testing purpose, you can always use the self-signed certificate that was generated from the above step.
Go to Thwate trial certificate request page and do the following:
- Select “SSL Web Server Certificate (All servers)” under the “select your trial certificate”.
- Do not check the PKCS #7 check-box under the “configure certificate”
- Copy/Paste the *.csr file that you generate above in the textbox under “certificate signing request (CSR)”
- Click on next at the bottom, which will give you a 21-day free trial certificate.
Copy/Paste the trial certificate to the www.thegeekstuff.com.crt file as shown below.
If you enjoyed this article, you might also like.
Next post: Google Chrome OS – Beginning of End of Microsoft?
Previous post: Blog Makeover: New Thesis Theme In Action
Important: This example is intended to provide general guidance to IT professionals who are experienced with SSL requirements and configuration. The procedure described in this article is just one of many available methods you can use to generate the required files. The process described here should be treated as an example and not as a recommendation.
I have purchased the SSL certificate from GoDaddy and i need to install this SSL certificate on siteground server because my site is hosted on siteground. But i am facing the issue with private key because when i try to set up the SSL certificate on Siteground it ask for private key and in am not. Ssl create private key file. How can I find the private key for my SSL certificate. If you just got an issued SSL certificate and are having a hard time finding the corresponding private key, this article can help you to find that one and only key for your certificate. An SSL Certificate is a public key verified and signed by a Certificate Authority. You generate a public/private key pair, then from that generate a Certificate Signing Request (which includes the public key), which you send to the CA. It then signs that public key included in the CSR producing the certificate which it sends back to you. What is a private key? All SSL Certificates require a private key to work. The private key is a separate file that’s used in the encryption/decryption of data sent between your server and the connecting clients. A private key is created by you—the certificate owner—when you request your certificate with a Certificate Signing Request (CSR). Jul 09, 2019 If the Private Key key file is lost, you’ll need to reissue your Certificate. Can I generate a new Private Key for my Certificate if I lose the old one? You can generate a new private key and CSR, or use the automatic CSR and key generation during Certificate reissue (this option is available for all Certificates except for the Multi.
When you configure Tableau Server to use Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) encryption, this helps ensure that access to the server is secure and that data sent between Tableau Server and Tableau Desktop is protected.
Looking for Tableau Server on Linux? See Example: SSL Certificate - Generate a Key and CSR.
Tableau Server uses Apache, which includes OpenSSL. You can use the OpenSSL toolkit to generate a key file and Certificate Signing Request (CSR) which can then be used to obtain a signed SSL certificate.
Ssl Certificate Generate Windows
Steps to generate a key and CSR
To configure Tableau Server to use SSL, you must have an SSL certificate. To obtain the SSL certificate, complete the steps:
- Generate a key file.
- Create a Certificate Signing Request (CSR).
- Send the CSR to a certificate authority (CA) to obtain an SSL certificate.
- Use the key and certificate to configure Tableau Server to use SSL.
Generate Ssl Key And Certificate Free
You can find additional information on the SSL FAQ page on the Apache Software Foundation website.
Configure a certificate for multiple domain names
Tableau Server allows SSL for multiple domains. To set up this environment, you need to modify the OpenSSL configuration file, openssl.conf, and configure a Subject Alternative Name (SAN) certificate on Tableau Server. See For SAN certificates: modify the OpenSSL configuration file below.
Set the OpenSSL configuration environment variable (optional)
To avoid using the -config argument with every use of openssl.exe, you can use the OPENSSL_CONF environment variable to ensure that the correct configuration file is used and all configuration changes made in subsequent procedures in this article produce expected results (for example, you must set the environment variable to add a SAN to your certificate).
Open the Command Prompt as an administrator, and run the following command:
set OPENSSL_CONF=c:Program FilesTableauTableau Serverpackagesapache.<version_code>confopenssl.cnf
Notes:
When setting the Open SSL configuration environment variable, do not enclose the file path with quotation marks.
If you are using a 32-bit version of Tableau Server on a 64-bit computer, run the
set OPENSSL_CONF=c:Program Files (x86)TableauTableau Serverpackagesapache.<version_code>confopenssl.cnfcommand instead.
Generate a key
Generate a key file that you will use to generate a certificate signing request.
Open the Command Prompt as an administrator, and navigate to the Apache directory for Tableau Server. For example, run the following command:
cd C:Program FilesTableauTableau Serverpackagesapache.<version_code>binRun the following command to create the key file:
openssl.exe genrsa -out <yourcertname>.key 4096Note: This command uses a 4096-bit length for the key. You should choose a bit length that is at least 2048 bits because communication encrypted with a shorter bit length is less secure. If a value is not provided, 512 bits is used.
Create a certificate signing request to send to a certificate authority
Use the key file you created in the procedure above to generate the certificate signing request (CSR). You send the CSR to a certificate authority (CA) to obtain a signed certificate.
Important: If you want to configure a SAN certificate to use SSL for multiple domains, first complete the steps in For SAN certificates: modify the OpenSSL configuration file below, and then return to here to generate a CSR.
Run the following command to create a certificate signing request (CSR) file:
openssl.exe req -new -key yourcertname.key -out yourcertname.csrIf you did not set the OpenSSL configuration environment variable,
OPENSSL_CONF, you might see either of the following messages:An error message about the config information being unable to load. In this case, retype the command above with the following parameter:
-config .confopenssl.cnf.A warning that the
/usr/local/ssldirectory cannot be found. This directory does not exist on Windows, and you can simply ignore this message. The file is created successfully.
To set an OpenSSL configuration environment variable, see Set the OpenSSL configuration environment variable (optional) section in this article.
When prompted, enter the required information.
Note: For Common Name, type the Tableau Server name. The Tableau Server name is the URL that will be used to reach the Tableau Server. For example, if you reach Tableau Server by typing
tableau.example.comin the address bar of your browser, thentableau.example.comis the common name. If the common name does not resolve to the server name, errors will occur when a browser or Tableau Desktop tries to connect to Tableau Server.
Send the CSR to a certificate authority to obtain an SSL certificate
Send the CSR to a commercial certificate authority (CA) to request the digital certificate. For information, see the Wikipedia article Certificate authority and any related articles that help you decide which CA to use.
Use the key and certificate to configure Tableau Server
Ssl Certificate Generate Private Key
When you have both the key and the certificate from the CA, you can configure Tableau Server to use SSL. For the steps, see Configure External SSL.
For SAN certificates: modify the OpenSSL configuration file
In a standard installation of OpenSSL, some features are not enabled by default. To use SSL with multiple domain names, before you generate the CSR, complete these steps to modify the openssl.cnf file.
Open Windows Explorer and browse to the Apache conf folder for Tableau Server.
For example:
C:Program FilesTableauTableau Server<version_code>apacheconfOpen openssl.cnf in a text editor, and find the following line:
req_extensions = v3_reqThis line might be commented out with a hash sign (#) at the beginning of the line.
If the line is commented out, uncomment it by removing the # and space characters from the beginning of the line.
Move to the [ v3_req ] section of the file. The first few lines contain the following text:
# Extensions to add to a certificate request
basicConstraints = CA:FALSE
keyUsage = nonRepudiation, digitalSignature, keyEnciphermentAfter the keyUsage line, insert the following line:
subjectAltName = @alt_namesIf you’re creating a self-signed SAN certificate, do the following to give the certificate permission to sign the certificate:
Add the
cRLSignandkeyCertSignto the keyUsage line so it looks like the following:keyUsage = nonRepudiation, digitalSignature, keyEncipherment, cRLSign, keyCertSignAfter the keyUsage line, add the following line:
subjectAltName = @alt_names
In the [alt_names] section, provide the domain names you want to use with SSL.
DNS.1 = [domain1]
DNS.2 = [domain2]
DNS.3 = [etc]The following image shows the results highlighted, with placeholder text that you would replace with your domain names.
 This cheat sheet style guide provides a quick reference to OpenSSL commands that are useful in common, everyday scenarios. IntroductionOpenSSL is a versatile command line tool that can be used for a large variety of tasks related to Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) and HTTPS (HTTP over TLS). This includes OpenSSL examples of generating private keys, certificate signing requests, and certificate format conversion.
This cheat sheet style guide provides a quick reference to OpenSSL commands that are useful in common, everyday scenarios. IntroductionOpenSSL is a versatile command line tool that can be used for a large variety of tasks related to Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) and HTTPS (HTTP over TLS). This includes OpenSSL examples of generating private keys, certificate signing requests, and certificate format conversion.Save and close the file.
Complete the steps in Create a certificate signing request to send to a certificate authority section, above.
Additional information
If you prefer to use a different version of OpenSSL, you can download it from Open SSL for Windows.